Pregnancies and Reproductive Services
Reproductive services include:
- Breeding Soundness Exams
- Genetic Testing and Counseling
- Ovulation Timing – Vaginal Cytology and Progesterone testing
- Breeding – Natural Breeding and Artificial Insemination
- Pregnancy Diagnosis and Puppy Counts – Relaxing Blood Test, Ultrasound, and X-Rays
- Pregnancy Support
- C-Sections
Dog and Cat Reproductive Services
There are few things in life more wonderful than a litter of happy, healthy puppies or kittens. The process of breeding, prenatal care, birth, and neonatal care, however, requires quite a bit of effort and dedication, and is not for everyone. We love to work with owners who are passionate about raising physically and emotionally healthy puppies and kittens and uniting them with loving families.
The process starts with selecting good candidates for breeding. A complete family history can reveal if an individual is likely to pass on genetic diseases or problems, and should be available from any reputable breeder. Depending on the breed, testing may also be available to evaluate for the presence of genetic diseases.
A thorough physical exam is essential to detect abnormalities that could be passed on to offspring or that could impair fertility or the ability to safely carry a pregnancy. A semen sample should be analyzed to confirm a male’s fertility. Temperament should also be carefully assessed, as some behavioral problems appear to have genetic components.
The key to successful conception in canines is in accurately timing a female’s ovulation, which allows for correctly timed breeding. The first step in ovulation timing involves monitoring vaginal swabs once a female goes into heat. These swabs reveal the change in cell composition that occurs with varying hormone levels. Once the cellular changes suggest ovulation is approaching, the blood progesterone level is tracked daily until it reaches the point at which ovulation occurs.
Breeding is planned for 48 hours after ovulation, and may be repeated 48 hours later. Both natural breeding and semen collection with immediate artificial insemination are options if the male resides locally. If the male lives far away, the chilled or frozen semen must be shipped the day before breeding is planned, so it arrives at the optimal time for artificial insemination.
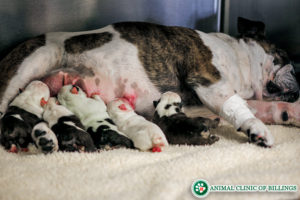
Pregnancy in both dogs and cats lasts about 60 days. There are two primary ways to confirm pregnancy. Starting at about 3 weeks after ovulation, a blood test that measures the level of relaxin, a hormone produced by the placentas, can be performed. Elevated levels indicate pregnancy, but do not provide any information about litter size.
About 4 weeks after ovulation, an abdominal ultrasound exam can identify the fetuses within the uterus, and can give an idea of the minimum number present. Once a female has been pregnant for 45 days, an abdominal x-ray will provide a more definitive count. Once pregnancy has been confirmed, special prenatal support measures, such as feeding changes and at-home monitoring, can be instituted as needed, and preparations can be made for the birth.
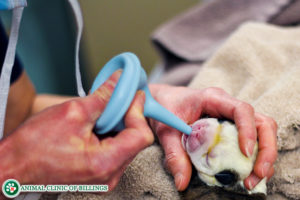
Most dogs and cats give birth without needing any help, but some breeds need assistance more commonly than others. Brachycephalic (“smooshed-faced”) breeds such as English Bulldogs, French Bulldogs, Pugs, and Boston Terriers, tend to have broad heads and narrow pelvises, making natural birth impossible for some individuals.
In these dogs, a C-section must be performed to deliver the puppies. This can either be scheduled in advance for a female’s natural due date, or performed once the female has gone into labor if delivery does not progress normally.
Toy breed dogs, such as Yorkies and Maltese, are also at increased risk of birthing difficulties. Regardless of breed, it is essential to closely monitor a female in labor in order to identify the earliest signs of possible trouble.

Once contractions have begun, a puppy or kitten should be delivered within 30 minutes. With the presence of continued contractions, subsequent deliveries should occur at least every 30 minutes.
A pause in contractions during labor may be observed, lasting up to 3 hours. Once contractions resume, the 30 minute guideline goes back into effect. If active contractions fail to result in a delivery in more than 30 minutes, if a female hasn’t had contractions for more than 3 hours, or if the female appears to be in distress at any point, urgent veterinary attention should be sought.

Let our highly trained and experienced team of veterinarians and veterinary technicians help you keep your dog as happy and healthy as they can be.
Call the Animal Clinic of Billings to schedule your dogs next wellness examination with us today!
406-252-9499 REQUEST AN APPOINTMENT